Database Schema
Our database schema is designed following the third normal form pattern (3NF). This structure provides the smallest footprint by ensuring that no data is duplicated and that in itself guarantees data integrity by avoiding inconsistent data across raw and aggregate data tables.
All data is constructed using primary and foreign key relationships, that further ensures integrity by preventing orphaned records, and by linking records using integers, provides critically fast queries using built-in table indexes and binary tree search algorithms. In addition, we further optimized the database by tuning it against the most common long running queries, using the information gained to construct additional indexes to allow even faster record retrieval.
Assets
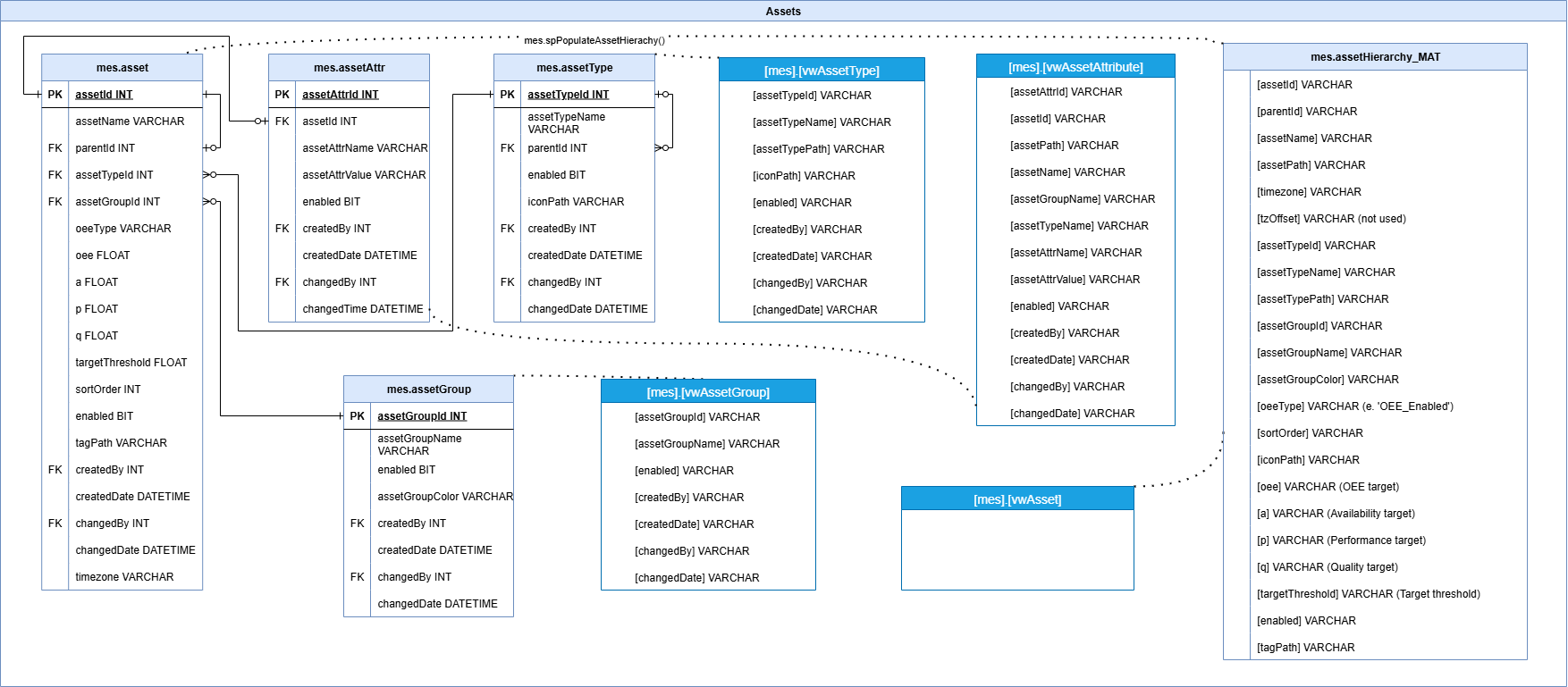
This group manages hierarchical structures of production assets, including lines, cells, and equipment. It includes support for asset types, locations, tag associations, and paths. This domain provides the foundation for all location- and asset-specific reporting.
Attributes
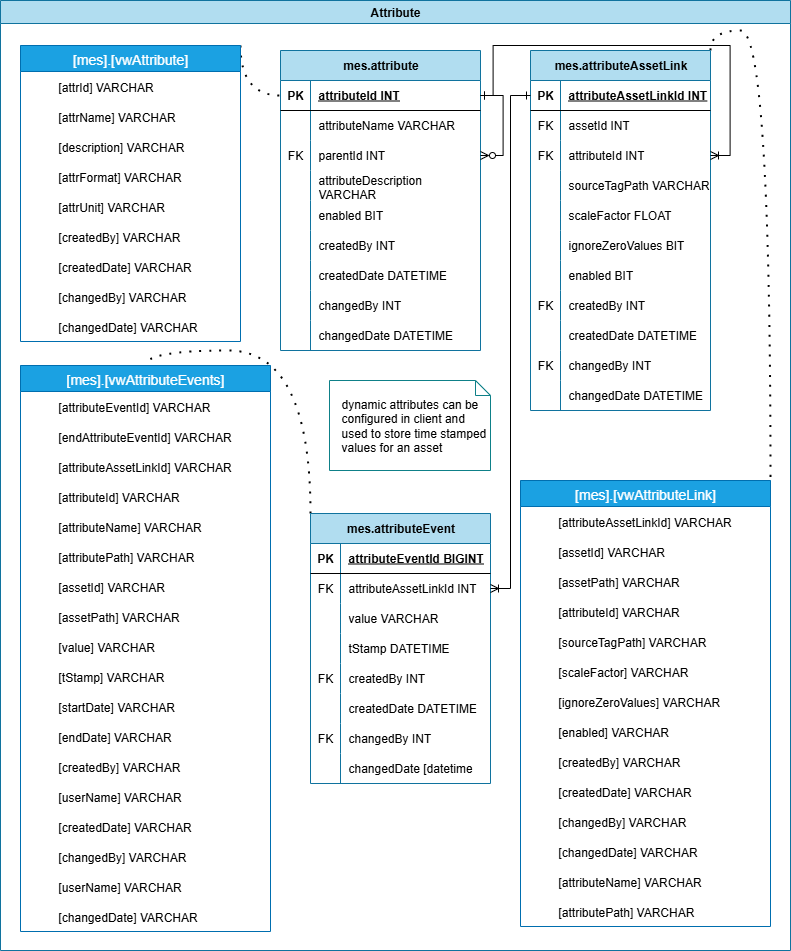
Attributes are derived or calculated values used to enrich raw data. This group defines attributes, links them to tag sources, and handles configurations like scale factors, zero filtering, and enablement status. Attributes are commonly used for KPIs, condition monitoring, and dashboards.
Counters
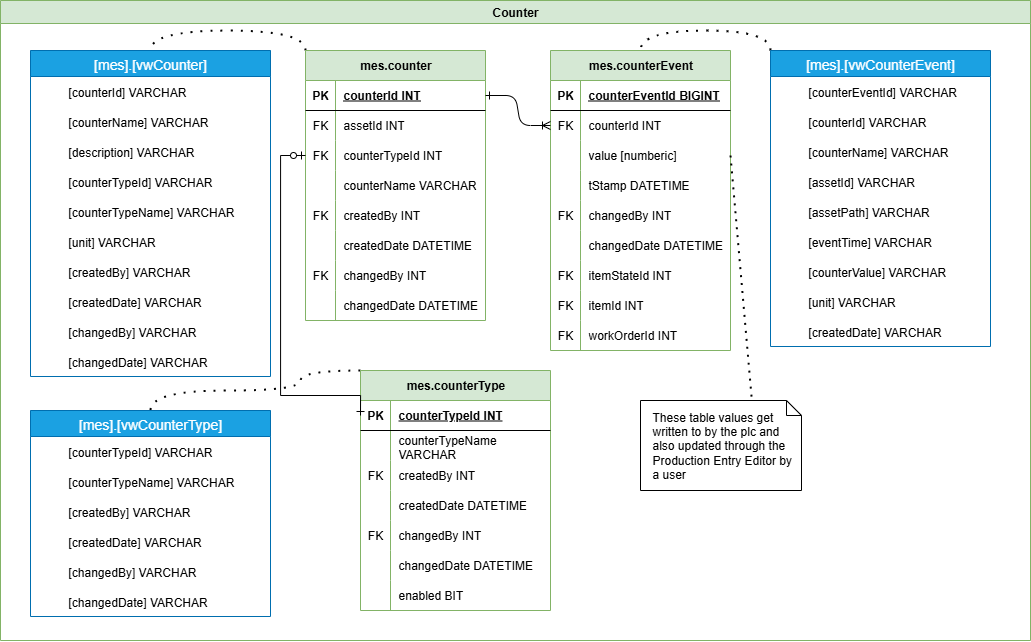
The Counters group records and configures count-based metrics such as part cycles, throughput, or error counts. It supports value logging, counter resets, and usage analytics tied to time, shift, and asset hierarchies.
Items
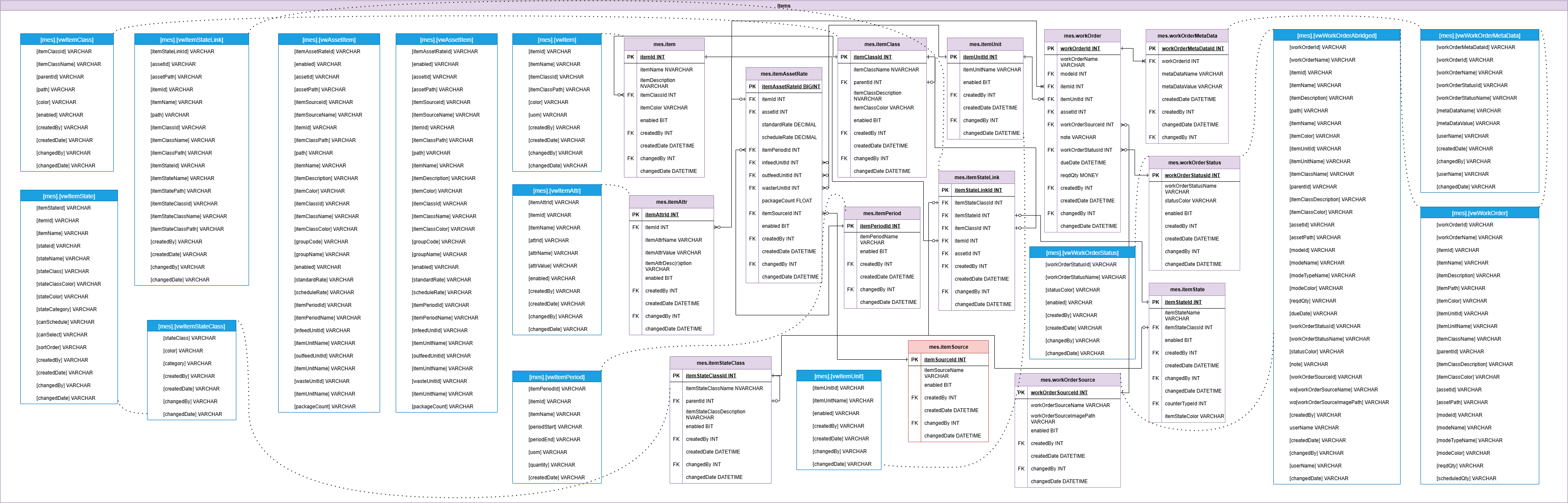
Defines SKUs, products, or part numbers manufactured or processed within the system. The Items group supports categorization, units, and product-specific configurations needed for run tracking, quality checks, and OEE calculations.
Lots
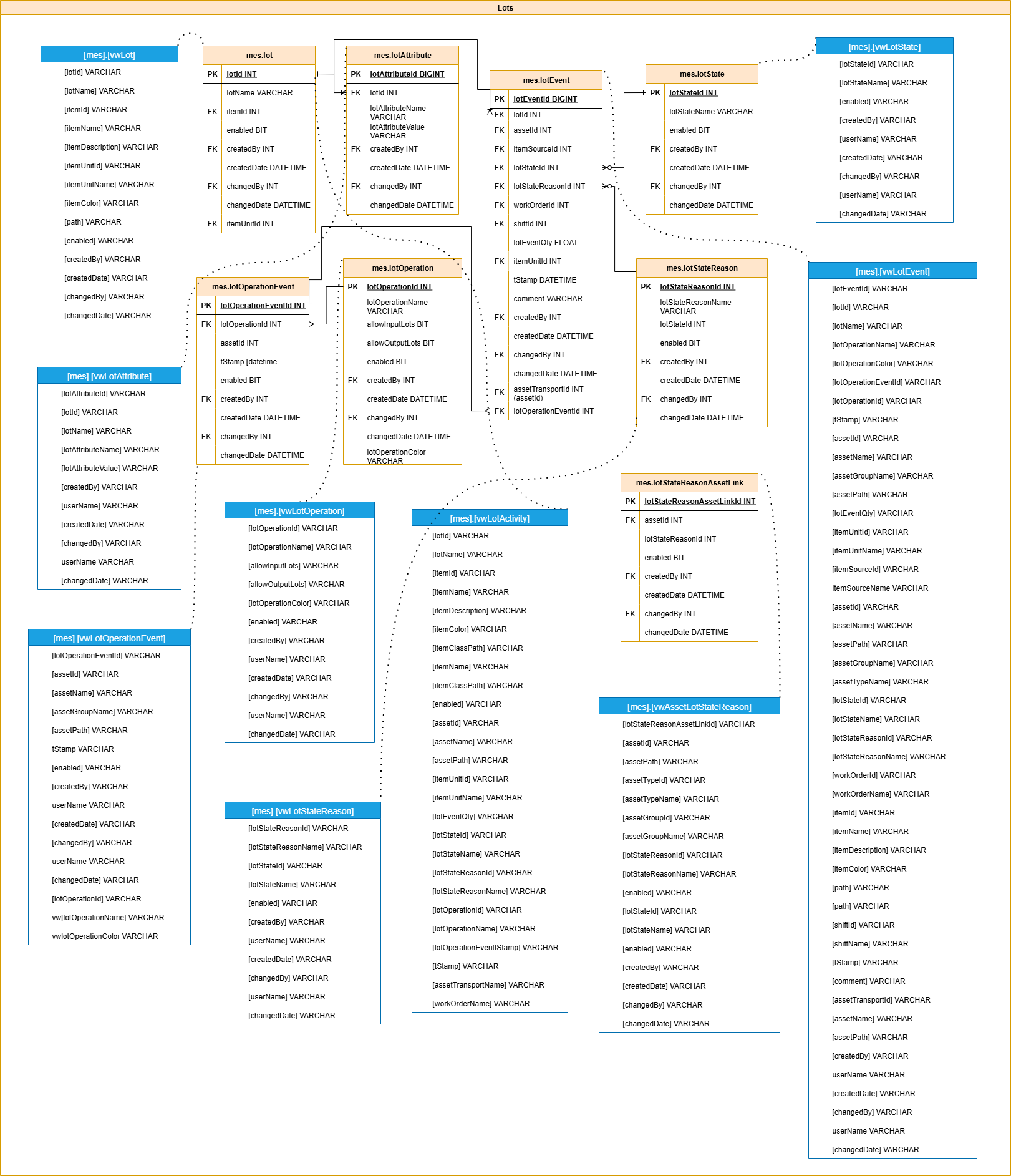
This group handles lot tracking—capturing traceability data across runs, shifts, and quality outcomes. It links lots to assets, timestamps, and product types to support compliance and recall readiness.
Modes
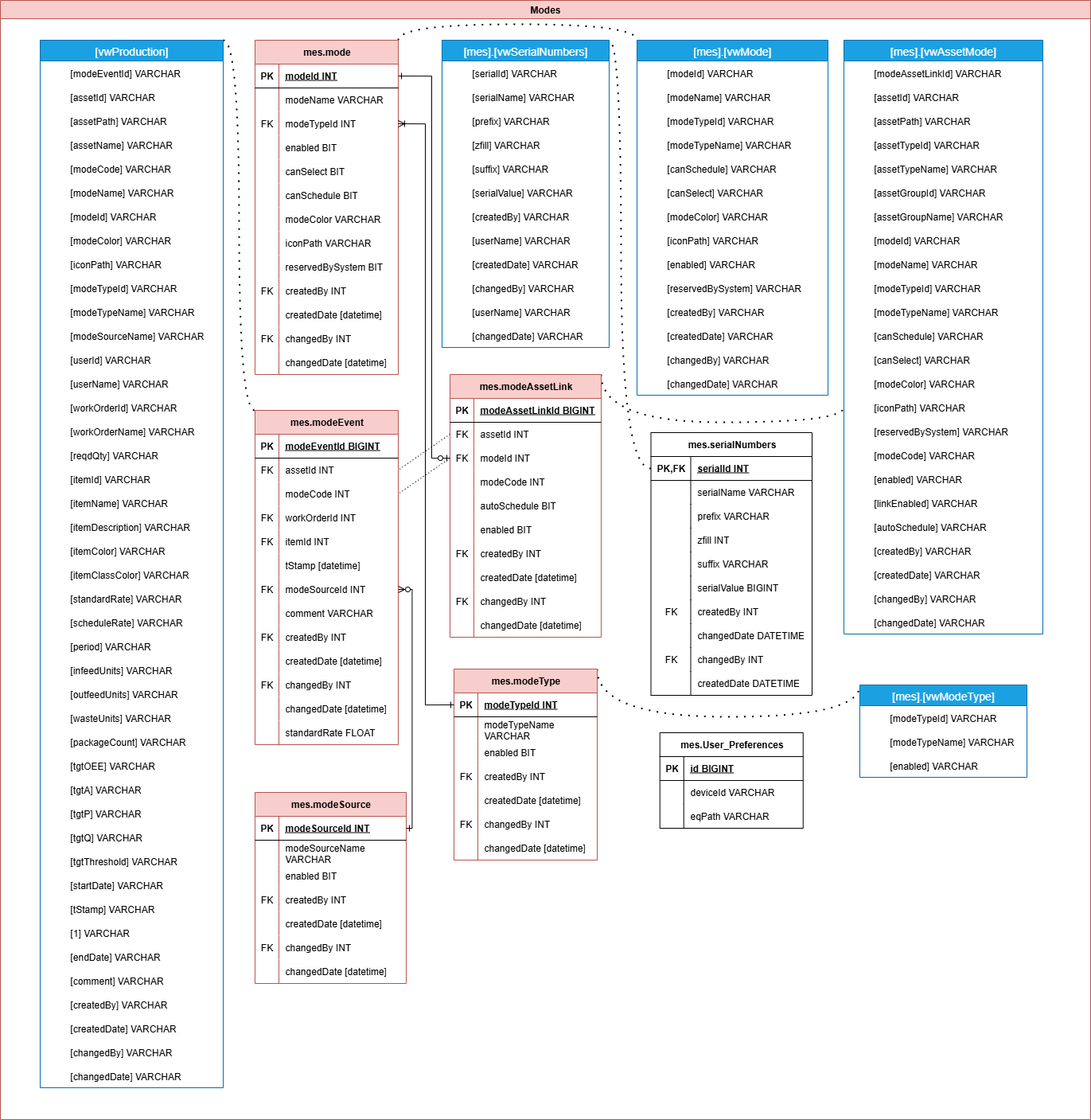
Tracks production modes or machine states such as "Running," "Idle," or "Setup." This data is essential for understanding line availability, state-based analytics, and root cause analysis of downtime or inefficiency.
States
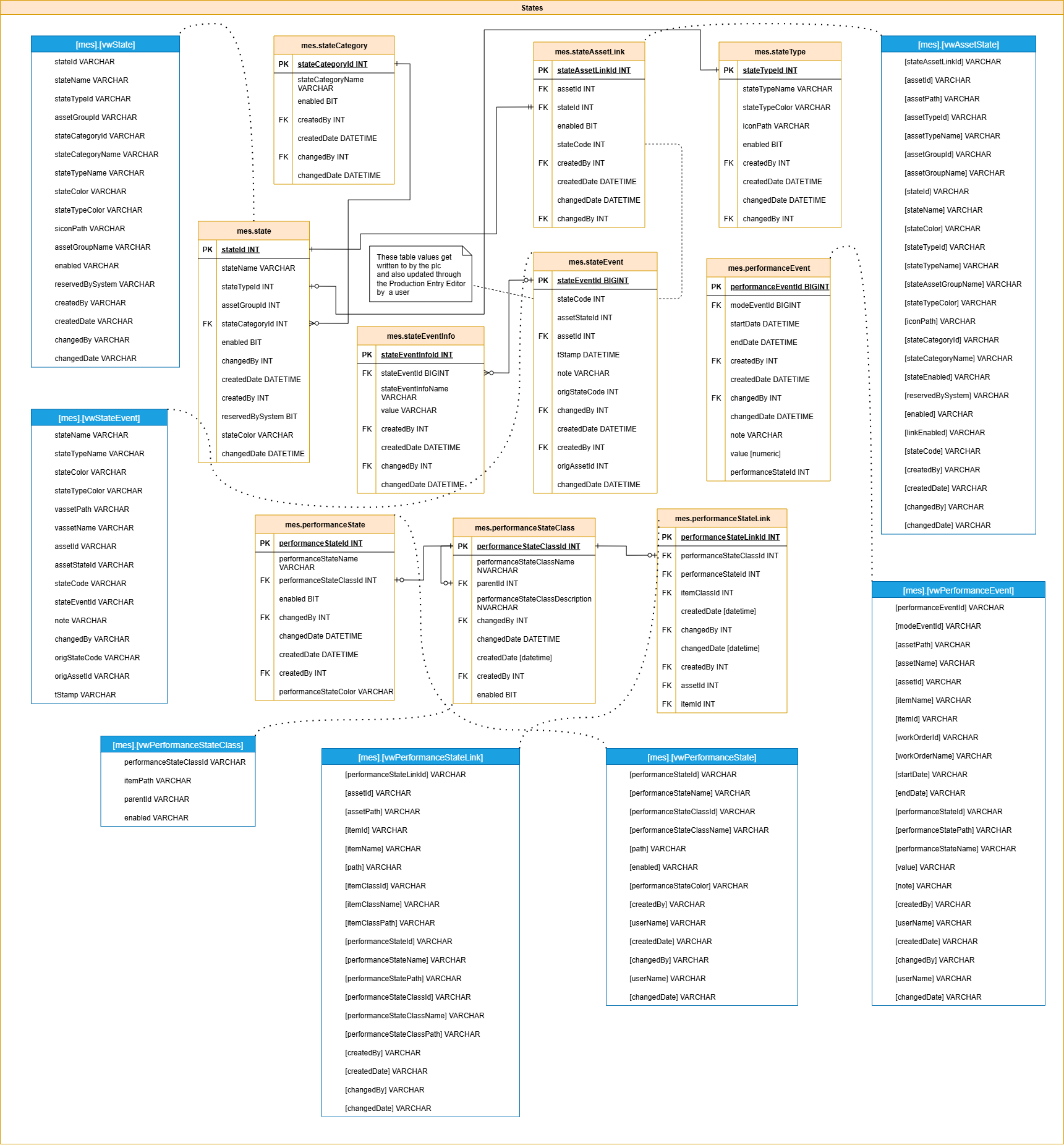
Defines and logs the operational state of lines and equipment. This group is foundational for dashboards and uptime metrics and often integrates with sensor signals or operator inputs to create accurate state timelines.
Core
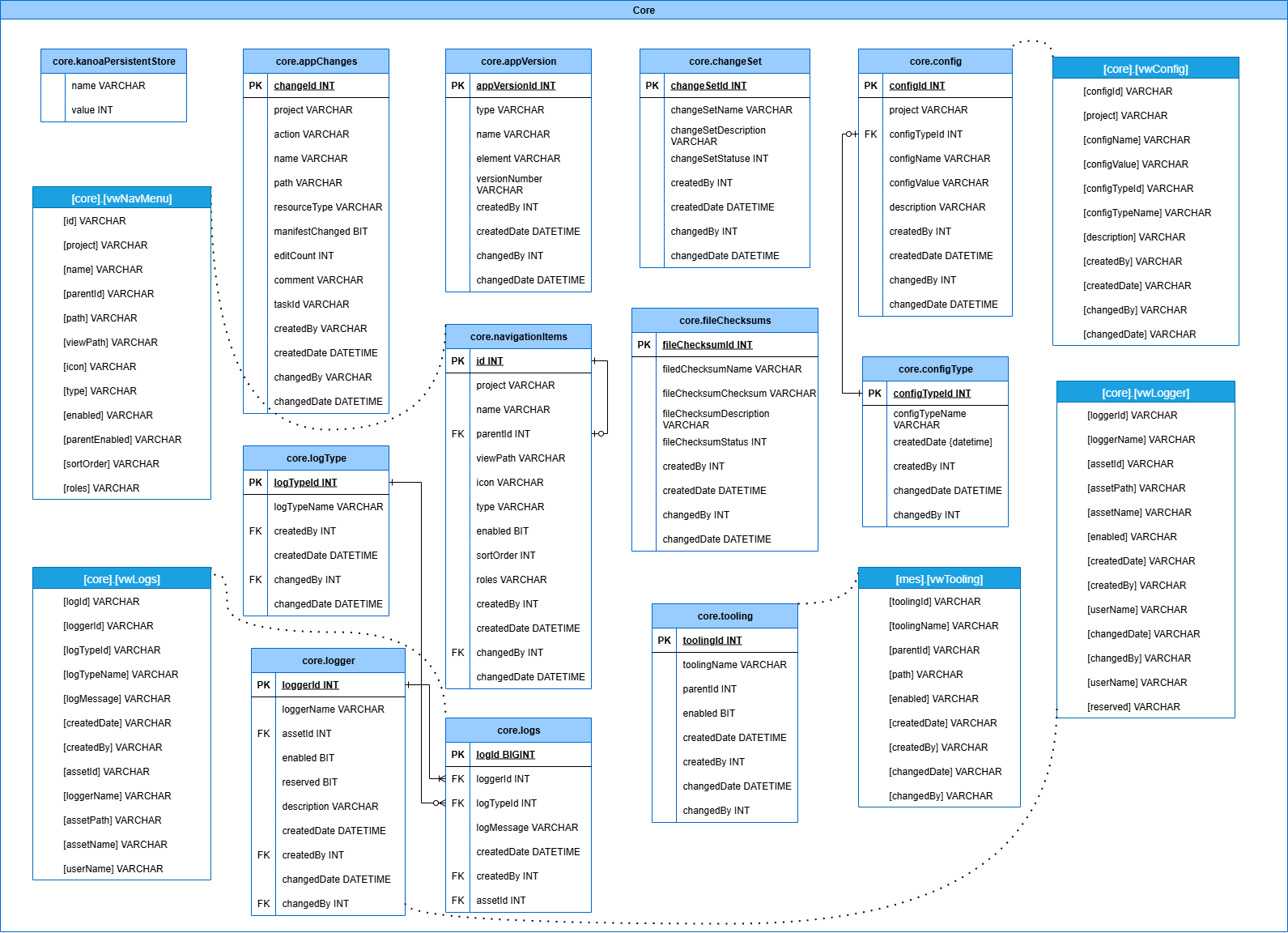
Contains system-level reference data and shared configurations like time intervals, shift structures, status codes, and enums. This group standardizes definitions across the database to ensure consistency and reduce duplication.
Dashboard
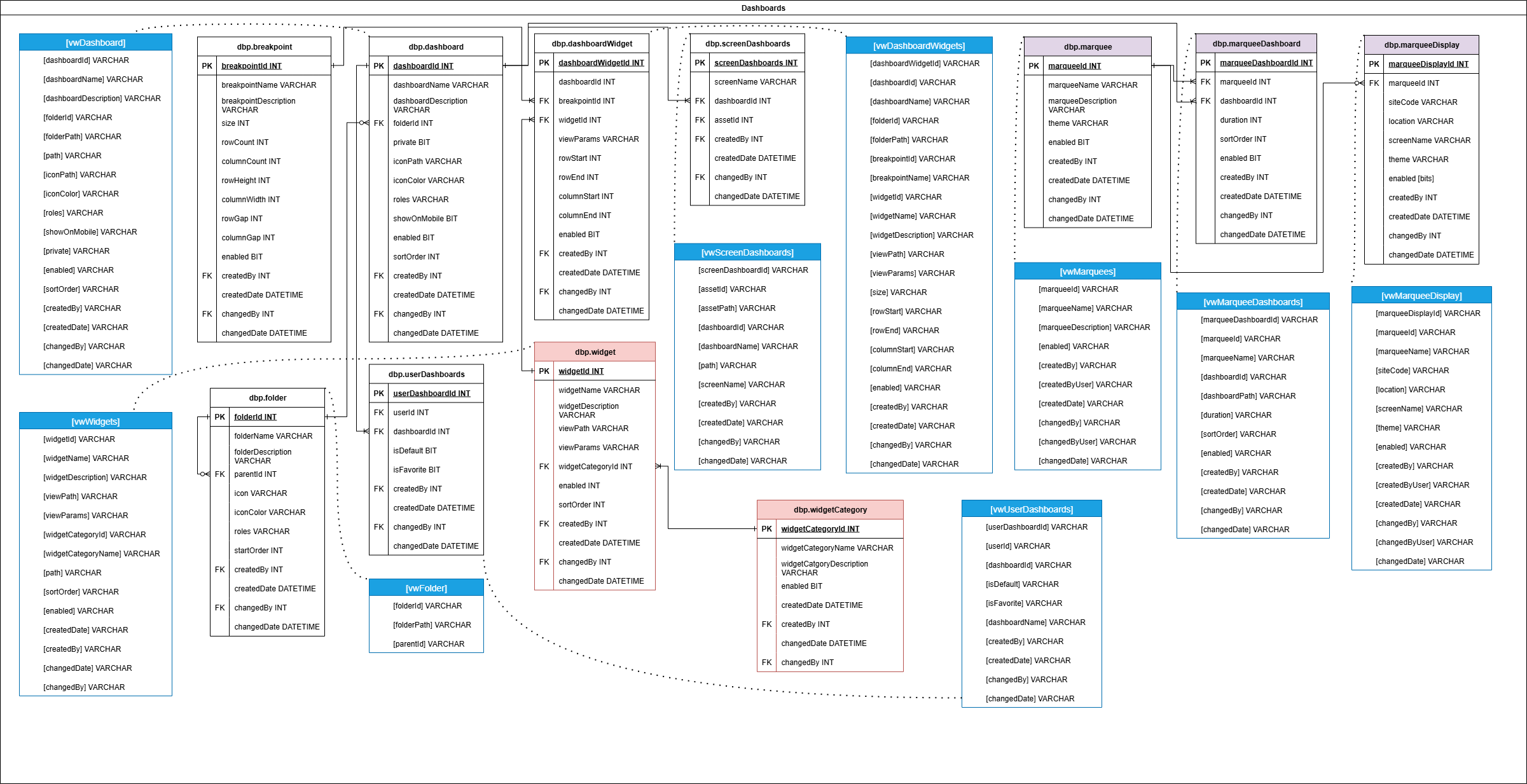
Provides support for custom dashboards, user-specific views, chart settings, and saved filters. This schema group enables tailored data exploration and KPI visualization across the platform.
Checks

Manages quality check definitions, thresholds, schedules, and result entry. It includes support for both manual and automated checks and allows for grouping checks by asset, shift, or product. Historical results can be used for compliance, alerts, or statistical process control.
QDS Attributes
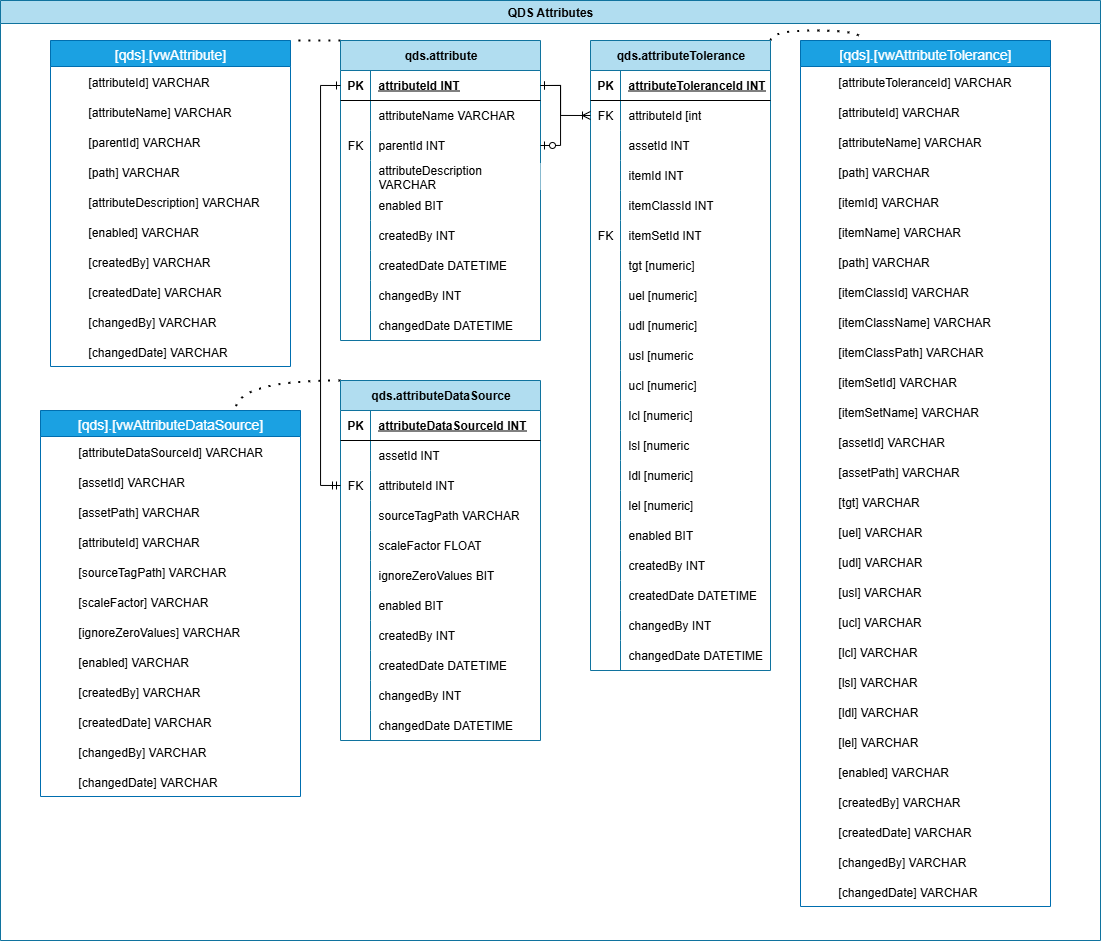
Supports the Quality Data System (QDS), with extended attributes designed for long-term quality tracking, versioning, and integration with external quality control platforms or regulatory audits.
Alerts
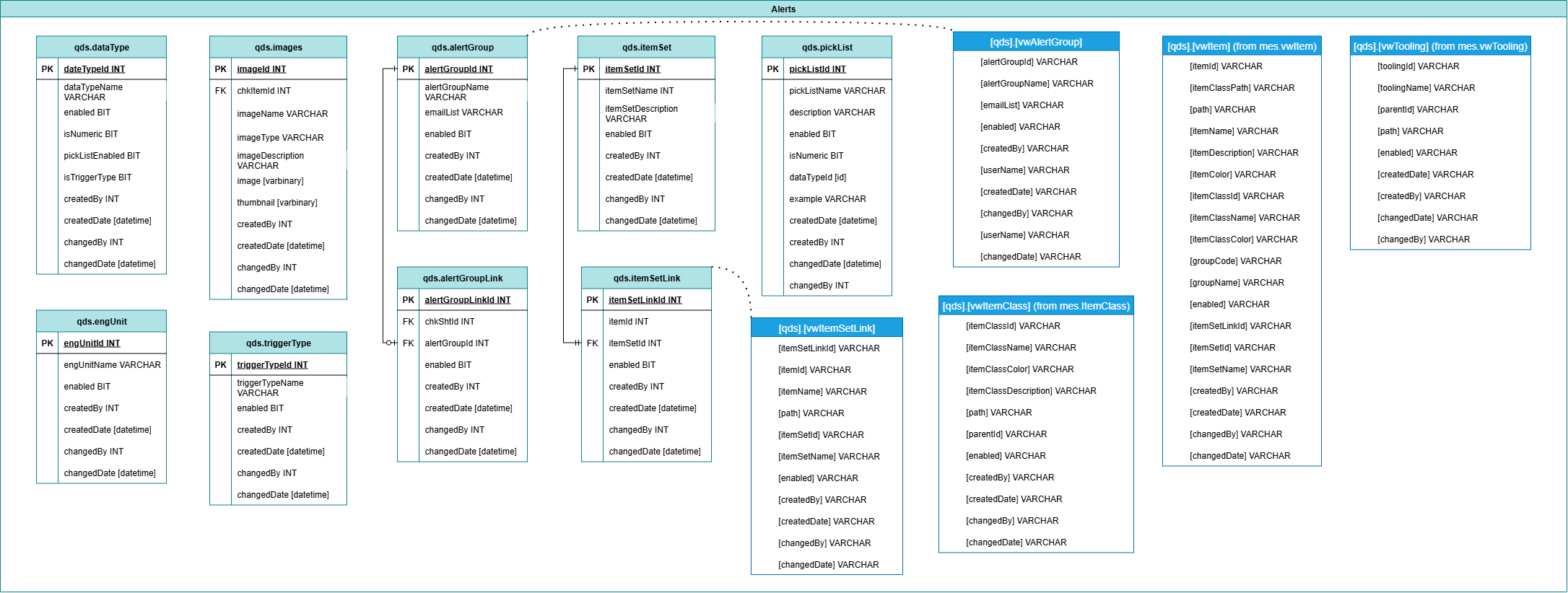
Manages alert definitions, triggers, and notification logic. Alerts are often tied to thresholds, event conditions, or quality rule violations and can be routed to users, logs, or external systems.
Schedule
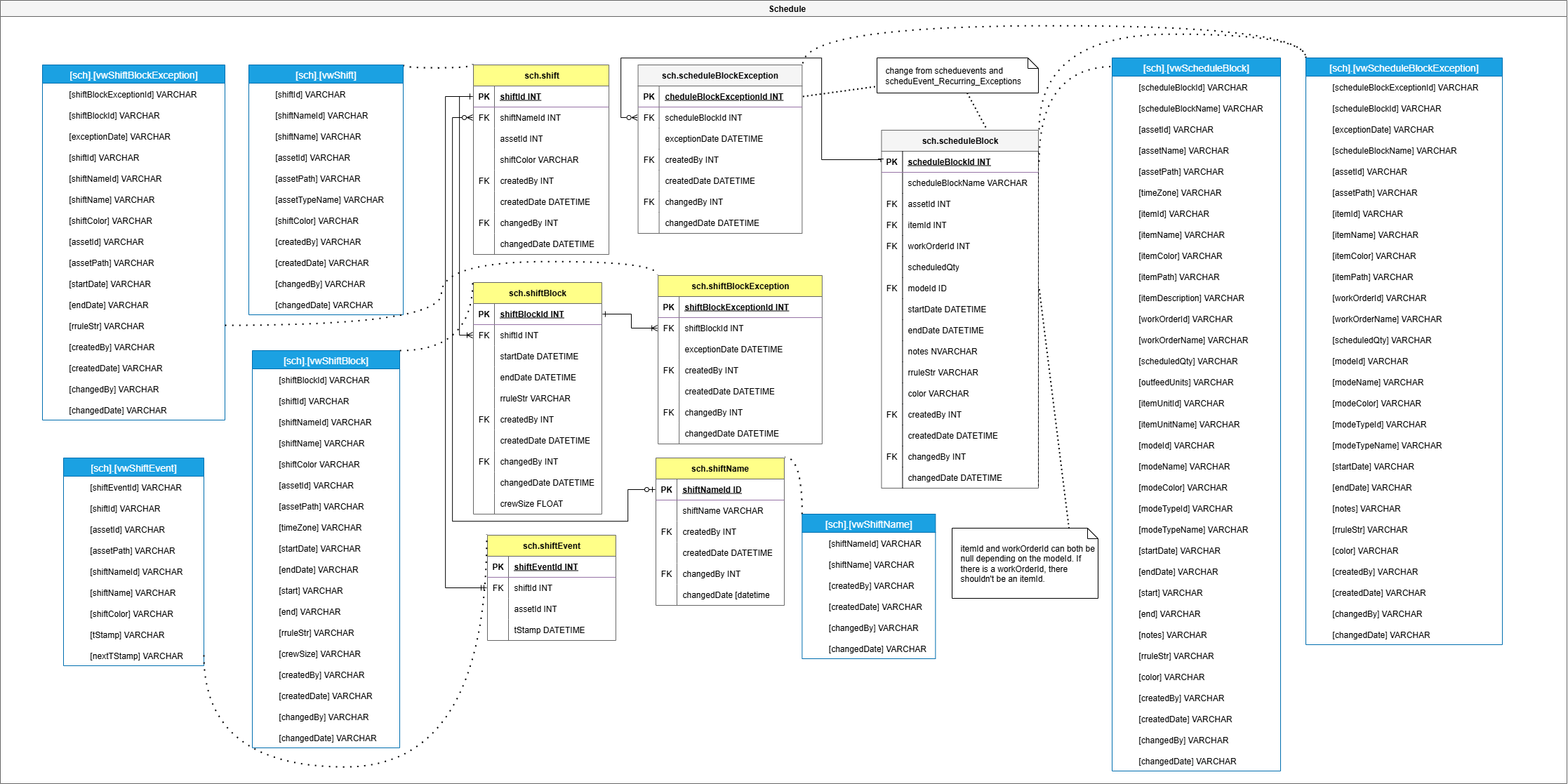
Handles time-based operations like check scheduling, downtime windows, and shift calendar events. This group ensures that time-aligned operations follow predefined business rules and intervals.
Security
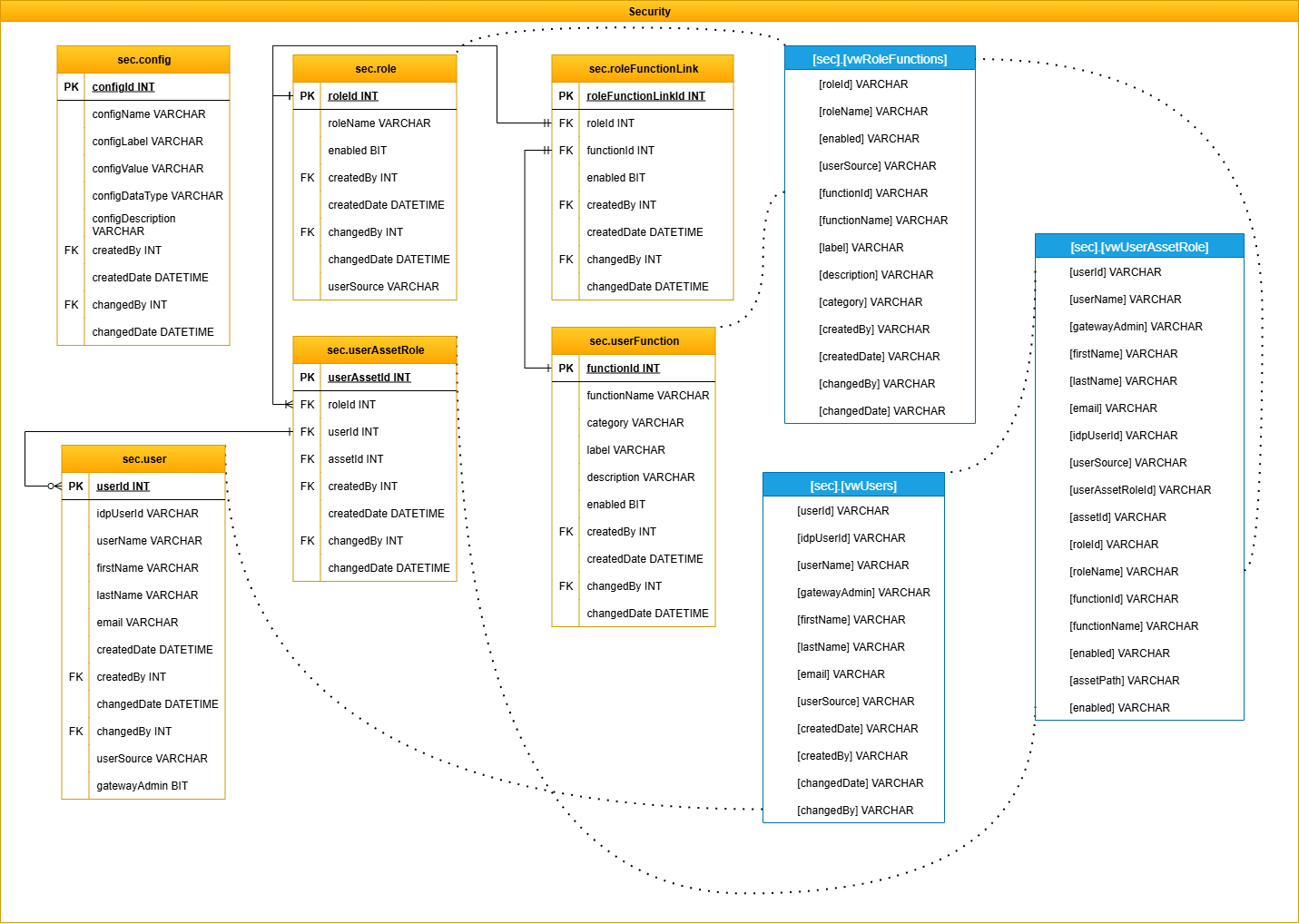
Implements role-based access control (RBAC) with users, roles, permissions, and group hierarchies. It also tracks changes, login activity, and site-level access restrictions to ensure operational security and compliance.